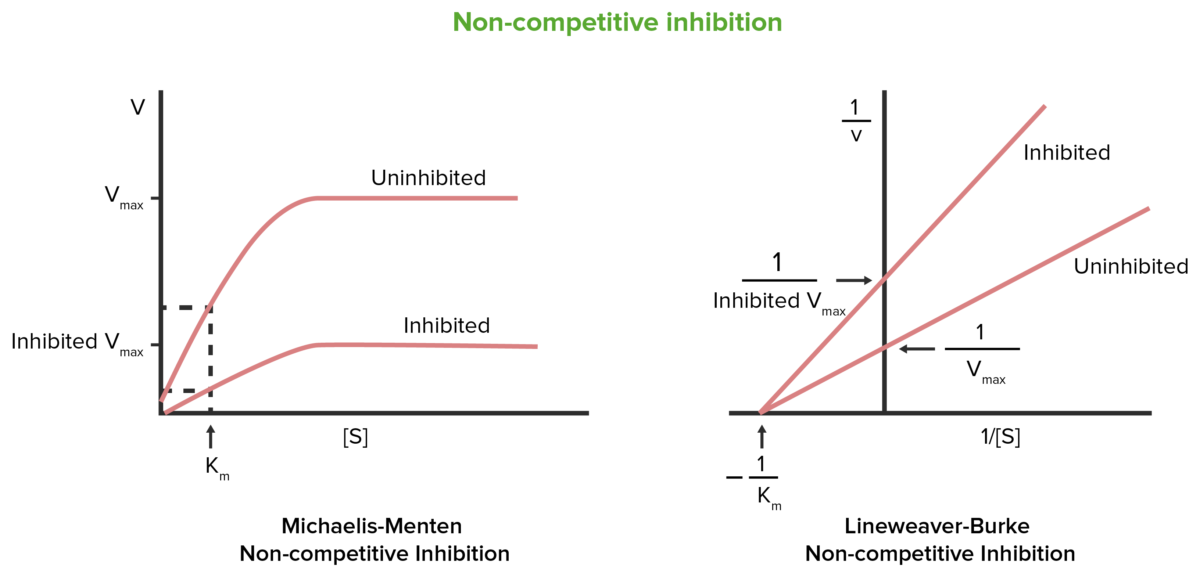
Mixed Inhibition Definition . mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. Time), v max is the upper. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition.
from www.lecturio.com
learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. Time), v max is the upper. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme.
Enzyme Inhibition Concise Medical Knowledge
Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. Time), v max is the upper. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs.
From www.onlinebiologynotes.com
Enzyme inhibition and types of enzyme inhibitors Online Biology Notes Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. the traditional model of general mixed. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.lecturio.com
Enzyme Inhibition Concise Medical Knowledge Mixed Inhibition Definition learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. Time), v max is the upper. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. See the mechanisms,. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation ID305372 Mixed Inhibition Definition define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.animalia-life.club
Mixed Inhibition Graph Mixed Inhibition Definition Time), v max is the upper. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent,. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.animalia-life.club
Mixed Inhibition Graph Mixed Inhibition Definition learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. Time), v max is the upper. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From jackwestin.com
Inhibition Types Control Of Enzyme Activity MCAT Content Mixed Inhibition Definition Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: Time), v max is the upper. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From dxoaogqyv.blob.core.windows.net
Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration at James Williams blog Mixed Inhibition Definition the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: Time), v max is the upper. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.pearson.com
Mixed Inhibition Channels for Pearson+ Mixed Inhibition Definition See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID305372 Mixed Inhibition Definition See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. Time), v max is the upper. the traditional model of general. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT to class of Enzyme and Inhibition PowerPoint Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. mixed inhibition is a type of. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT LECTURE 2 ENZYME PowerPoint Presentation, free download Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. Time), v max is the upper. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme PowerPoint Presentation ID305372 Mixed Inhibition Definition define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From dxoaogqyv.blob.core.windows.net
Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration at James Williams blog Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. the traditional model of general mixed. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From dxojsfdfj.blob.core.windows.net
Competitive Inhibition Mechanism at Donald Gregory blog Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. Time), v max is the upper. See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. the traditional model of general. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From pediaa.com
What is the Difference Between Competitive and Mixed Inhibition Definition See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. Time), v max is the upper. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From pediaa.com
Difference Between Reversible and Irreversible Enzyme Inhibition Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor can bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already. mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. learn how enzymes can be inhibited by various mechanisms, such as irreversible covalent, competitive, and noncompetitive. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From jackwestin.com
Inhibition Types Control Of Enzyme Activity MCAT Content Mixed Inhibition Definition mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from analogy to enzymes and their. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. mixed inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor. Mixed Inhibition Definition.
From pediaa.com
What is the Difference Between Competitive and Mixed Inhibition Definition See the mechanisms, equations, plots and examples of. the traditional model of general mixed inhibition is: mixed and noncompetitive inhibition this represents the case where the inhibitor can bind both to the free enzyme. Where v is the speed of the reaction (slope of product formed vs. define agonist, partial agonist, antagonist, and mixed (noncompetitive antagonists) from. Mixed Inhibition Definition.